Structures of the Nervous System
The nervous system has numerous component parts. The main structures are summarized in the diagram below:
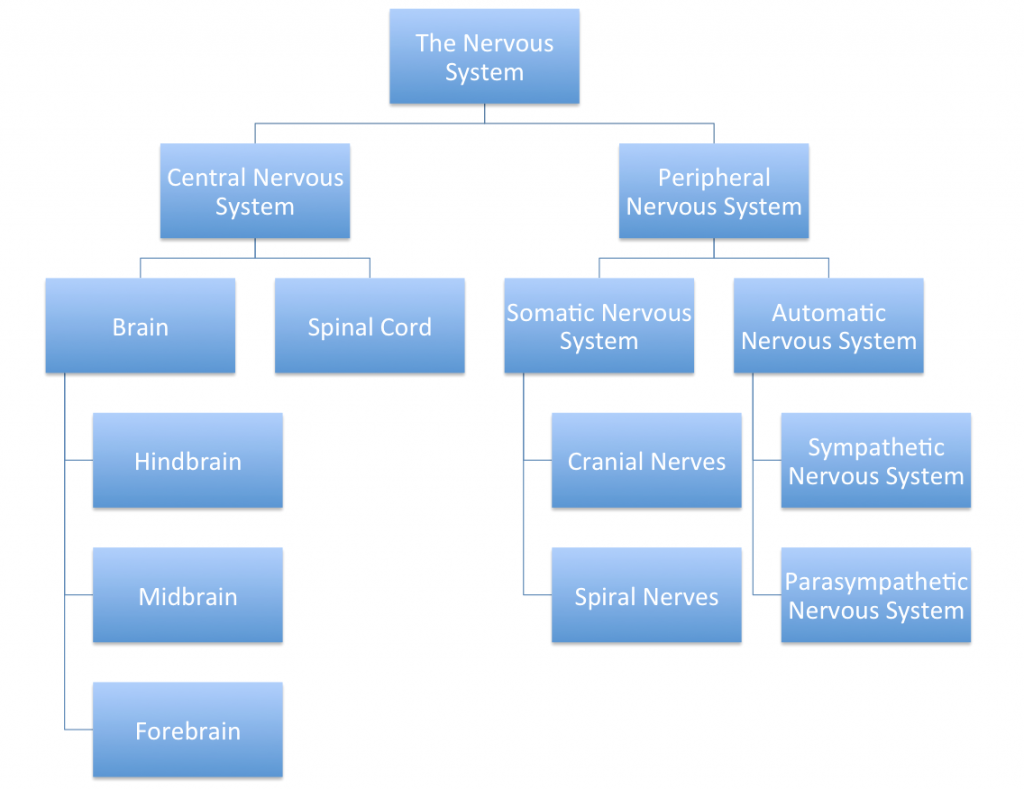
The Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system is the body system responsible for sensing events in the environment or from within ourselves, to process and integrate the information, and to respond.
Table of Functions
|
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM To sense events in the environment or from within the body, to process and integrate the information, and to respond. |
|
Peripheral Nervous System The part of the nervous system which detects changes in the external environments and from within the body. |
|
Somatic Nervous System This component of the nervous system is responsible for conscious and voluntary movement. It comprises various nerves. · Sense receptors in the eyes, ears, skin, mouth, nose, and internal organs. · Nerves from the sense organs to the central nervous system (sensory nerves). · Nerves from the central nervous system to the peripheral organs (motor nerves). · The nerves arising from the head are called cranial nerves, and those from the spinal cord are called spinal nerves. |
|
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) The ANS controls involuntary body processes, such as heart rate, breathing, digestion, salivation, sweating, etc |
|
Sympathetic Nervous System The component of the ANS which activates the body for reaction to danger, emergency situations, or stress. It is the well-known fight, flight, or freeze reaction. Autonomic responses include · increased heart rate · sweating · dry mouth · cessation of digestive activity (feeling of butterflies in the stomach) · muscle tension · shallow rapid breathing · high level of mental focus, · state of fear and panic. |
|
Parasympathetic Nervous System The component of the ANS which develops when the individual is relaxed and free from stress. The features of this state include: · Reduced heart rate · relaxed muscles · reduced sweating · normal digestive and elimination activity · warm relaxed feeling · deep/slow/abdominal breathing |
|
Central Nervous System |
|
Spinal Cord · Receives information from the senses and relays to the brain. This is the ascending pathway. · Relays commands from the brain to muscles, glands, and other organs. This is the descending pathway. · Controls reflex responses. |
|
Brain · Hind-brain, Midbrain, forebrain. · Forebrain: Occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes |
